We have all developed the COMMIT framework to comprehensively address the aspects where we need to undertake responsibility and mitigate climate, air, water, waste and biodiversity-related risks. The COMMIT model enables futureproofing of natural assets across our operations and our stakeholder’s ecosystem.






First step in Marico’s climate-first business agenda is to reduce organisational GHG emissions. We have developed a robust carbon management strategy that prioritises actions related to energy efficiency, fossil fuel avoidance, renewable energy transition, carbon forestry and reduction of carbon footprint across our product’s life cycle.
Marico has adopted the target of achieving net-zero emissions across global operations by 2040.

Reduce Scope 1 and Scope 2 GHG emissions by 93%, and offset remaining 7% emissions through sequestration, and carbon offset by 2030, from the baseline year FY13.
A systematic GHG inventory is maintained to identify and quantify all direct and indirect (Scope 1, 2 and 3) emissions from our operations and value chain. We aim at gradually imbibing each unit into the transitional pathway of carbon neutrality by optimising their energy footprint, investing in low-carbon technology to minimise operational emissions, switching to renewable sources of energy to meet operational requirements, and opt for local carbon sinks to sequester carbon for offsets.
Purchased from EB
Solar
Wind
Furnace Oil
Diesel
Biomass
Gas
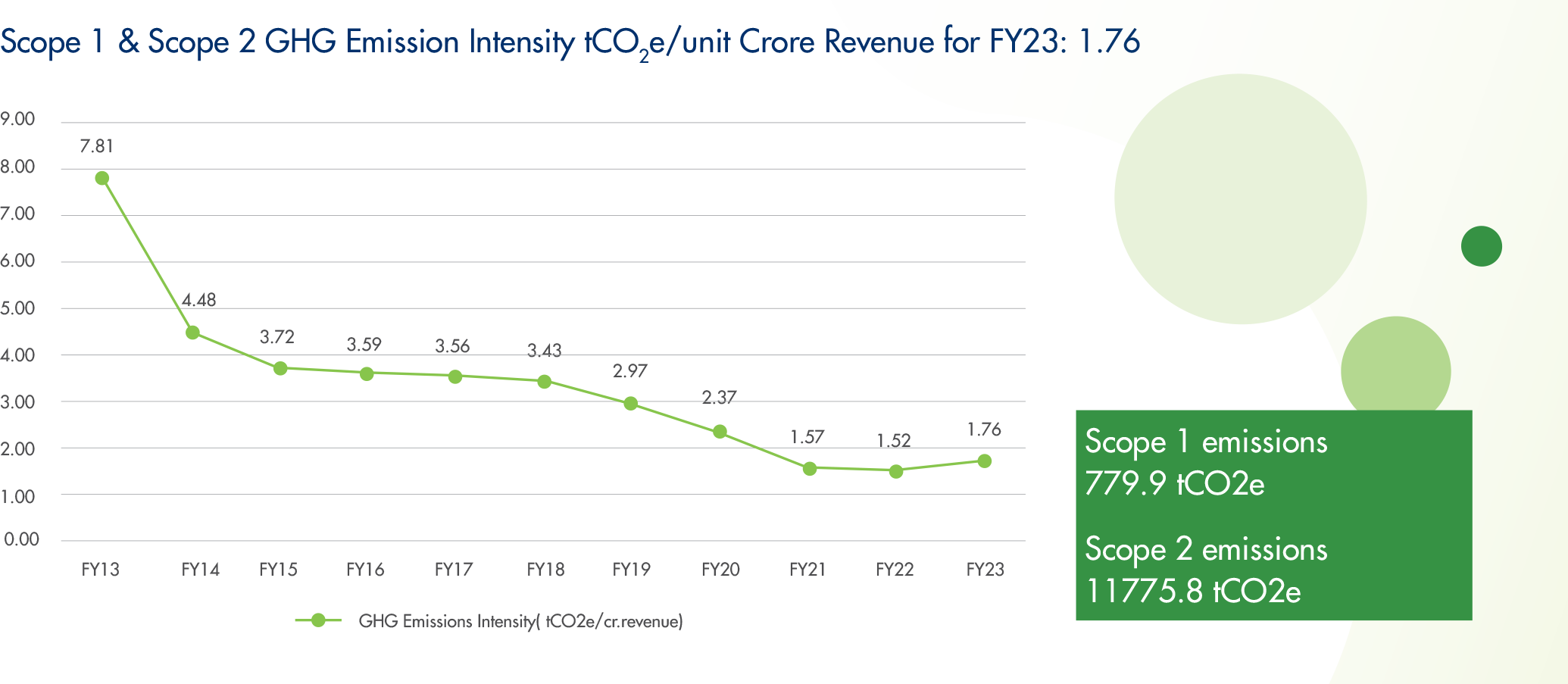
Steady decrease in y-o-y GHG emission intensity is attributed to our constant ef forts to improve operational efficiencies, adoption of energy saving mechanisms, use of clean fuel like bio-briquettes, and inclusion of renewable energy in our portfolio.
These efforts have also helped us to over-achieve the set emission reduction target, despite a growing manufacturing footprint.

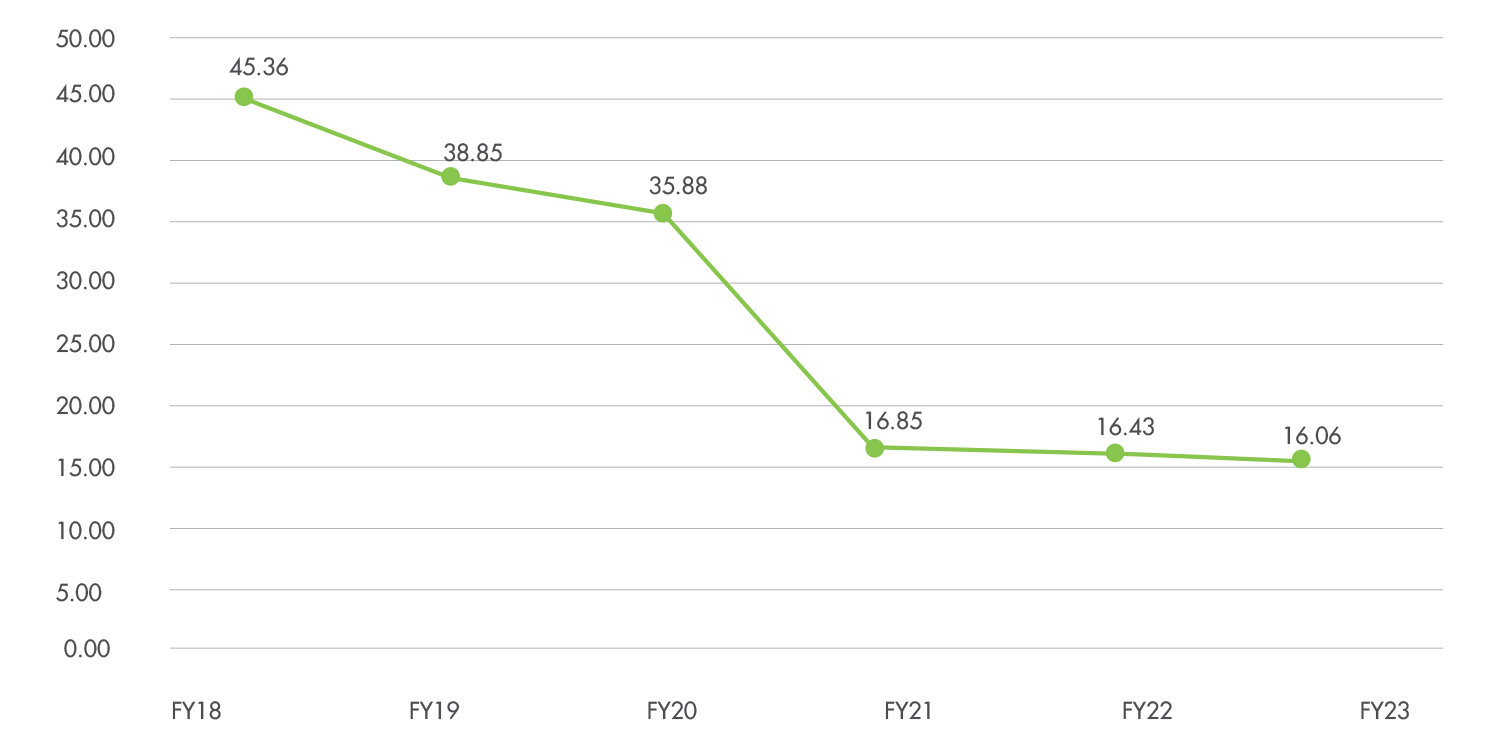
More than 95% of our overall GHG emission is contributed by Scope 3 emissions. We calculate Scope 3 emission footprint of the entire organisation by compiling relevant category- wise emissions data. The reporting boundary of each Scope 3 category is limited to ‘operational influence’. Emission factors for each material or fuel are referred from the Greenhouse Gas Protocol.
In FY23, the Scope 3 GHG emissions for India operations stood at 5,47,126 tCO2e, resulting in ~12% reduction in Scope 3 Emission Intensity as compared to base year FY19.
We adopt quantifiable and pragmatic reduction targets on a short, medium and long-term basis through optimisation of business-related travels, reconfiguration of logistics footprint, sustainable packaging solutions, recycling and reuse of waste, and joining forces with critical value chain partners to implement green projects.

| Scope 3 Emission Category | Description | tCO2e |
|---|---|---|
| Category 1 Purchased Goods |
All our raw and packaging materials are covered under this cate gory | 4,10,168 |
| Category 2 Capital goods |
Emissions resulting from purchase of capital goods | 695 |
| Category 3 Fuel Activities |
Total quantity of fuel consumed in operations is co | 4,421 |
| Category 4 Upstream Transportation |
Distance between source and destination points for transportation of raw materials, packaging materials, and finished goods, is considered | 53,368 |
| Category 5 Waste Generated |
Quantities of different categories of waste generated in operations are considered | 8,226 |
| Category 6 Business Travel |
Details of emissions pertaining to total distance travelled by air, rail, and road, for business, are considered | 1,403 |
| Category 7 Employee Commuting |
Average distance between office and employee residence is considered, along with total number of employees and working days | 910 |
| Category 8 Upstream Leased Assets |
Energy utilisation of all our depots and relevant third-par ty manufacturing units is considered | 34,861 |
| Category 9 Downstream Transportation |
Average distance covered for transportation of finished goods from retailers to consumers is considered | 4,799 |
| Category 12 End-of-life Treatment |
Total quantity of post-consumer waste generated through packaging materials is considered | 27,989 |
| Category 15 Investment |
Emissions from investments | 287 |
Marico’s Perundurai facility is certified as ‘carbon neutral’ since FY20. The plant operates on 100% renewable energy and utilises smart energy installations to further optimise operational efficiency.
As reduction in GHG emission is a key objective for us, we initiated many projects to reduce overall emissions intensity. Of the total GHG emission in FY23, more than 90% emissions were contributed by electricity consumption in manufacturing units. To reduce these emissions, Marico has initiated solar and wind projects in Sanand and solar expansion project Jalgaon, which have a potential of reducing annual GHG emissions by 3500 tCO2e and 400 tCO2e, respectively.

We are steadily enhancing the percentage of renewable energy in our operations in a phased manner. The thermal energy requirement is fulfilled by bio-based briquettes, making renewable energy (for heating purpose) contribute 99% of the total thermal energy used across operations. The remaining thermal energy requirements are being met from Piped Natural Gas (PNG), and High-Speed Diesel (HSD).


Our Sanand plant in Gujarat is one of the most advanced facilities. Recently, it has received the IGBC Platinum certification by the Indian Green Building Council. A holistic approach of energy efficiency has been considered in the project buildings with regard to the envelope, systems, lighting and other equipment.
The project achieved
of energy savings and
Solar panels of capacity
are installed to generate
of the annual non-process energy requirement.
The plant uses
for the HVAC equipment.
The project has used materials with recycled content, which constitute
of the total cost of the construction materials.
of building materials sourced locally.
compliance are met with fresh air requirements for airconditioned and forced ventilated spaces.
of the total floor area of all regularly occupied spaces meet the IGBC daylight levels.
The central energy management cell works on a defined energy reduction strategy in conformity to the business goals and targets set for every year. Energy monitoring systems accurately capture the minutest reduction opportunities across the operational footprint.
Through a set of strategically designed ideation sessions, energy management projects are executed throughout the year. Every change in process and equipment is checked for energy consumption against standards, while decision making. The energy reduction framework that is followed across Marico’s operational landscape is illustrated here:

We laid the foundation of our water stewardship strategy in FY18. The ‘Jalashay’ programme is a product of this strategy, through which, we seek to offset our water consumption by creating water storage potential for communities in water stress regions across the country. The programme undertakes water conservation activities such as dam desilting, rejuvenation of water bodies and the construction of farm ponds.
The manufacturing units operate on the principles of zero liquid discharge (ZLD) model, and the entire volume of industrial effluents is recycled within the operational boundaries of our facilities, utilising the treated water for administrative and gardening purposes. We harvest rainwater within our boundaries to reduce freshwater consumption.
Over
water capacity created in FY23, compared to total consumption in operations
Crore litres of water capacity created till date
Over
Farm ponds constructed in FY23
At Marico, we have developed a product sustainability index (PSI) to benchmark product sustainability. PSI enables us to integrate, implement and measure sustainability objectives on a single platform, transforming it into a business that delights consumers and accelerates eco-conscious consumerism.
Our target is to integrate sustainability considerations across products’ lifecycle (encompassing ingredient/material selection, sourcing, manufacturing, supply chain and end use), ensure 100% compliance on product quality, ingredient safety, transparent disclosure on product formulations and accelerate consumer-centric product innovation to improve nutritional value of products.
We have conducted cradle-to-grave life cycle assessment of 31 products across our product range, including hair oils, fabric care, food and vegetable oils. The studies were conducted by an independent external agency as per applicable ISO standards and standard global guidance available on LCA.
The key sustainable packaging interventions undertaken in FY23 include:


Opportunity was identified to reduce carbon footprint by reduction in bottle and cap weight in rigids.
Emission reduction by

Opportunity was identified to reduce carbon footprint by optimising tertiary packing through reduction in CFC weight and primary packing head space.
Emission reduction by
Our PSI framework enables us to identify, manage and mitigate impacts related to sustainability in every stage of the product life cycle, from sourcing, to designing, manufacturing, transportation, distribution, and end-life disposal. The aim of this framework is to foresee the potential environmental and social impacts of our products and inform our decision-making. With PSI, we are institutionalising innovation within organisation and across stakeholders.
Reduce the overall environmental and social footprint of our products


Establish traceability
Ensure 100% compliance on product quality, ingredient safety


Accelerate consumercentric product innovation to improve its health and nutritional benefits

*PSI draws reference from multiple international frameworks, research-based publications, and ecolabel certifications. It measures the sustainability footprint of products as well as benchmarking them against some of the renowned world-class standards on product sustainability.
At Marico, we have developed a product sustainability index (PSI) to benchmark product sustainability. PSI enables us to integrate, implement and measure sustainability objectives on a single platform, transforming it into a business that delights consumers and accelerates eco-conscious consumerism.
Our target is to integrate sustainability considerations across products’ lifecycle (encompassing ingredient/material selection, sourcing, manufacturing, supply chain and end use), ensure 100% compliance on product quality, ingredient safety, transparent disclosure on product formulations and accelerate consumer-centric product innovation to improve nutritional value of products*

Some noteworthy projects conducted in FY23 towards minimising operational environmental risks include:
Marico’s Sanand unit, Gujrat With water stress becoming a pertinent risk across the world, businesses and communities are facing disruptions due to unavailability or inadequacy of freshwater for their regular use. Water consumption reduction is a focus area to conserve freshwater resources for future.
Marico Sanand unit completed a project to reduce the water consumption in boiler operations by optimizing the blow down frequency of the boiler, reducing idle operating time, and improving the feed water quality by filters.
This project reduces the freshwater intake of the boiler section by about 350 KL/year and improving the plant’s overall water intensity.
Marico’s Sanand unit, Gujarat Rich biodiversity is an indicator of healthy ecosystem that supports revitalising activities of our planet through natural processes. Exercising the principles of biodiversity conservation, we have developed a Miyawaki forest within the periphery of our Sanand facility.
Around 24000 trees of 60 different species planted in Miyawaki forest covering close to 10 thousand sq. mtr. area which purifies surrounding air. We attempt to sustain the forest through optimal usage of resources and processes that have minimal environmental footprint like using organic fertilizers, recycled water etc.
Marico’s Sanand unit, Gujarat Waste reduction is a key aspect of continuous improvement, as it helps to save costs, resources, and environmental impacts. Reducing waste means avoiding or minimizing the generation of waste in the first place. The process improvement project would reduce wastes in business operation.
The process improvement project undertaken is in line with Marico’s commitment of reducing waste. Sanand factory identified several actionable points to reduce the operational wastages and successfully closed the gaps. This resulted in more than 46% & 47% savings of raw materials and packaging materials when compared to the consumption of same period for FY22.
At Marico, we are committed towards embedding circularity in our packaging portfolio and extending our efforts beyond regulatory mandates.
Marico’s Upcycle program is designed to integrate the principles and key performance metrics related to circularity within our overall packaging portfolio. A set of 9 opportunity levers have been established to accomplish the 2030 goals that have been set towards this material topic.

Plastic, one the most light-weight protective material, is widely used for wrapping and encasing products. Our research and development team works on solutions to curtail the wastage of plastic, and transition to recyclable, reusable and compostable plastic packaging material. We are gradually incorporating recycled plastic content in packaging. The plastic recovered from waste is converted into granules, and utilised in the production of packaging materials.
Value added hair oils
Opportunity was identified to reduce carbon footprint by dosing recycled- PET with virgin-PET in few SKU’s of Value Added Hair Oils rigids.
Opportunity was identified to reduce carbon footprint by using recycled LDPE in place of virgin LDPE as secondary packaging for certain products of value added hair oils.
Virgin PET consumption reduction by 130 MT during FY23.
Virgin LDPE consumption reduction by 23 MT during FY23
In alignment with the Plastic Waste Management (PWM) Rules, 2018 and the national guidelines on Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) released in 2022, we have carried out collection, recycling, co-processing, and safe disposal of 18,584 MT of post-consumer waste, including multilayer plastic (MLP), rigid and flexible plastic in FY23.
To ensure timely completion of our EPR activity, and confirm that handling, recycling, disposing, and documentation processes of our waste management agencies (WMAs), are in line with government norms, we appoint competent external agency to conduct independent third-party audit for selected WMAs and recyclers.
We are incorporating sustainable practices throughout the value chain through SAMYUT, our responsible sourcing programme. Through SAMYUT, we seek ethical responsibility from our value chain partners in the realm of legal and regulatory compliance, social responsibility and environmental responsibility.
We are seeking 100% legal and regulatory compliance on environmental and social aspects from our partners.
Our business associates are evaluated for environmental management practices in our value-chain, with focus on following practices:
The SAMYUT framework, at Level 1, facilitates education and awareness amongst our value chain partners on best practices, and encourage the partners to self-declare their environmental performance. Progressively, at Level-2, Value chain partners are audited on given environmental criteria. For selected suppliers, Marico aim to undertake joint projects and technical know-how to pilot best practices.
Through SAMYUT, we are also establishing transparency in our value chain and tracing our raw materials from source. Currently, we are establishing traceability mechanism in our coconut value chain in southern India.
To scale-up our circularity-based interventions within and beyond the sectoral boundaries, Marico decided to join hands with the India Plastics Pact, a transformational and collaborative platform created by WWF India and CII, anchored at the CII-ITC Centre of Excellence for Sustainable Development (CESD), with support from WRAP, a global NGO based in the UK.
Marico is a founding member of the India Plastic Pact. Our packaging strategy is aligned with the Pact’s 2030 vision.
